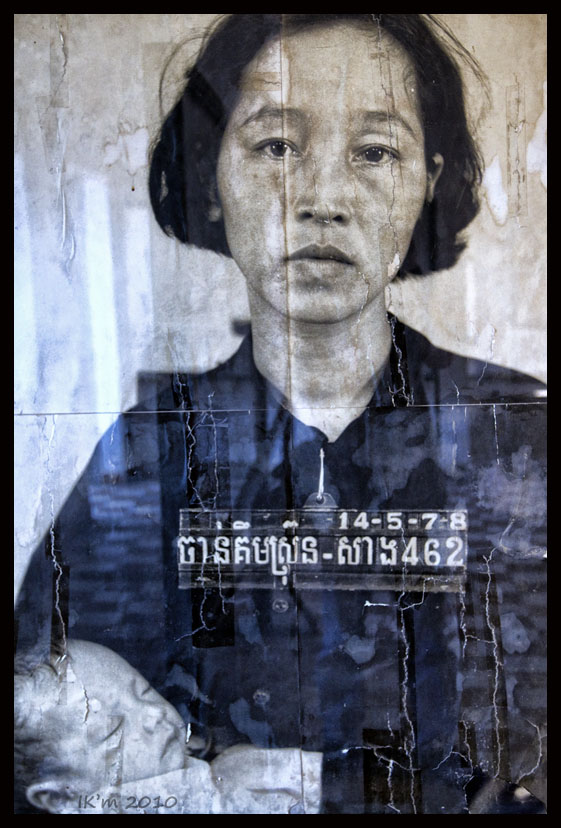
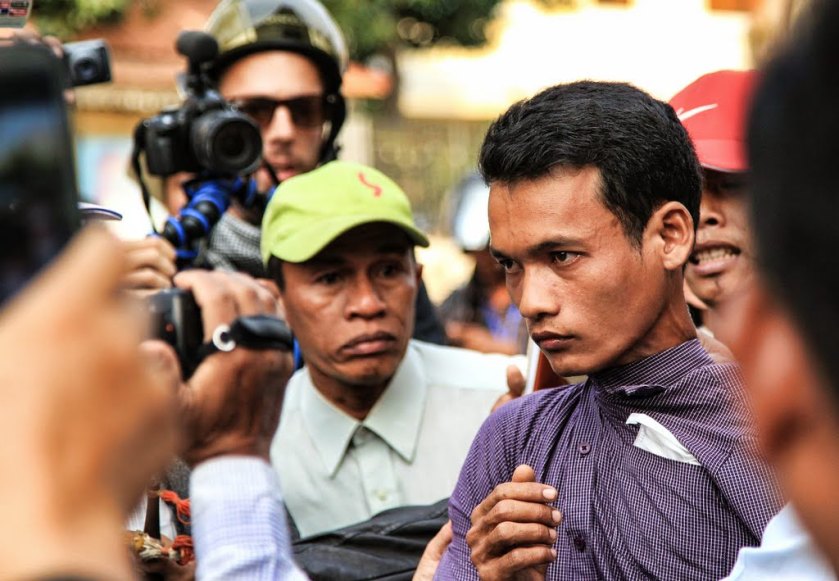
Publishing shocking images is neither inherently right nor wrong—it depends on intent, context, and consequence. The ethical challenge lies in balancing public interest with personal dignity, truth with sensitivity, and impact with responsibility.
Photojournalism often confronts us with the raw edge of reality—war, disaster, injustice, grief. These images can jolt viewers into awareness, spark outrage, and mobilise change. But they can also retraumatise, exploit, or misrepresent. So when is it right to publish a shocking image—and when is it wrong?
✅ When It’s Justified
- Public interest outweighs discomfort: Images that expose systemic abuse, corruption, or humanitarian crises may be shocking—but they serve a vital civic function.
- Truth is preserved: If the image is accurate, unmanipulated, and contextually honest, it contributes to informed discourse.
- Consent is considered: When possible, subjects should be aware of how their image will be used—especially in vulnerable situations.
- Impact is constructive: If the image leads to policy change, aid mobilization, or cultural reckoning, its shock may be ethically warranted.
❌ When It’s Problematic
- Sensationalism overrides substance: If the image is published for clicks, not clarity, it risks exploitation.
- Subjects are dehumanised: Graphic depictions that strip away dignity or reduce people to symbols of suffering cross ethical lines.
- Context is missing: A shocking image without background can mislead, stigmatise, or distort public understanding.
- Harm outweighs benefit: If the image retraumatises survivors, endangers individuals, or incites hate, it should be reconsidered.
🧭 Ethical Guidelines for Publishing Shocking Images
- Caption with care: Provide factual, neutral context to guide interpretation.
- Blur or anonymise when needed: Protect identities in sensitive situations.
- Seek editorial review: Run controversial images past peers or editors before publishing.
- Reflect before release: Ask: Would I feel respected if this were me?
🧠 Final Thought
Shocking images have power—but power without ethics is dangerous. The goal of photojournalism is not to numb or exploit, but to awaken and inform. Publishing such images demands courage, but also compassion. The question is not just can we publish—but should we. And that answer must be earned, not assumed.
Would you like this adapted into a visual manifesto or ethics card for your portfolio?
Publishing Shocking Images: Right or Wrong
Shocking images command attention, accelerate public debate, and can catalyze change — but they also risk exploitation, retraumatisation, and distortion. Deciding whether to publish such images is an ethical judgment as much as an editorial one, requiring clear criteria, transparency, and a commitment to minimizing harm.
What we mean by shocking images
Shocking images are photographs that provoke strong emotional reactions because they show violence, suffering, severe injury, or intimate moments of distress. They differ from disturbing journalism in degree and immediacy: their visceral impact can both illuminate and overwhelm a story.
Arguments for publishing
- Public interest and accountability: Graphic images can document abuses and provide evidence when other records are absent; they can mobilize public opinion and spur policy or humanitarian response.
- Bearing witness: Photographers and news organizations sometimes cite a duty to show realities that would otherwise be unseen, arguing that sanitizing imagery risks erasing the urgency of certain crises.
- Truth-telling value: When used responsibly, stark images can convey truths that words alone cannot, making abstract harms tangible for audiences.
(These benefits depend on accurate captioning, strong sourcing, and editorial restraint to ensure images inform rather than manipulate.)
Arguments against publishing
- Exploitation and dignity: Shocking images can reduce people to objects of spectacle, stripping context and agency from victims and survivors.
- Harm and retraumatization: Graphic exposure can cause further trauma to subjects, their families, and communities; publication can have long-term consequences for those depicted.
- Manipulation and loss of trust: Cropping, sequencing, or sensational captions can distort meaning and erode public trust in journalism; visual shock for clicks undermines credibility.
Ethical criteria to apply before publishing
- Public interest test — Does the image materially inform the public or hold power to account, beyond mere sensationalism?.
- Dignity check — Can the subject’s dignity be preserved through framing, captioning, or anonymisation?.
- Harm assessment — What are the likely short- and long-term harms to the subject, family, or community? Can those harms be mitigated?.
- Provenance and accuracy — Is the image verified, honestly captioned, and placed in proper context?.
- Alternatives — Could less graphic visuals, stills, or descriptive reporting achieve the same public interest goal with lower harm?.
Apply these in sequence: fail any single test, and the case for publication weakens considerably.
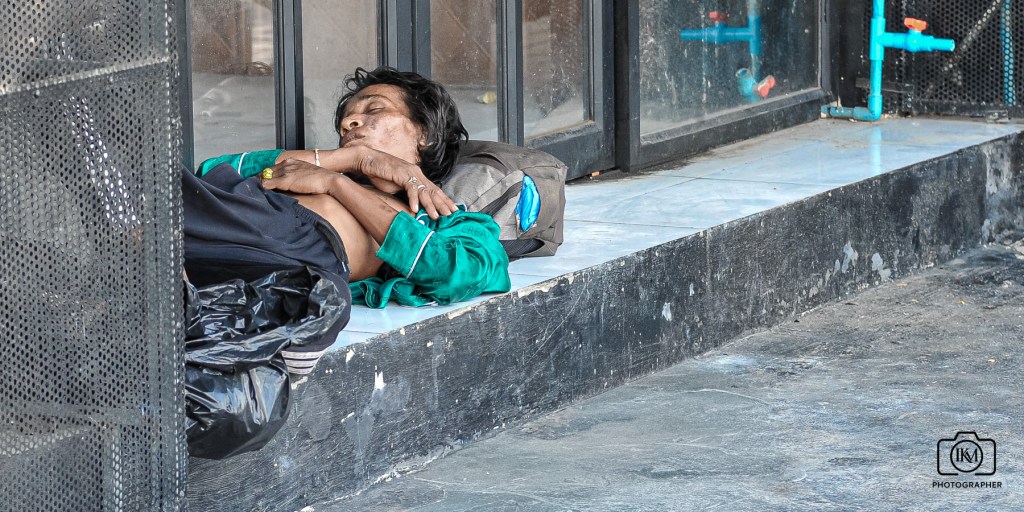

Practical editorial guidelines
- Use clear, factual captions that state who, what, where, when, and why; avoid sensational language.
- Consider cropping or blurring to preserve identity and dignity without erasing the essential truth.
- Offer warnings and placement choices (e.g., not lead-story fronting on social feeds) so audiences can consent to exposure.
- Disclose edits and sourcing when relevant; transparency builds trust.
- Use peer review or editorial oversight for borderline cases, and consult legal counsel when publication could create liability or danger.
Conclusion
Publishing shocking images can be ethically defensible, but never automatic. The default should be caution: ask whether the image serves a clear public interest, whether it preserves human dignity, and whether harms have been reasonably mitigated. When journalists and editors apply rigorous verification, contextualization, and harm-conscious practices, graphic images can illuminate truth and prompt change; without those safeguards, they risk exploitation and eroded trust